ASEAN Summit
Table of Contents
About ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional inter-governmental organization formed to promote economic growth, peace, and cultural cooperation among Southeast Asian countries.
- Founded on: 8 August 1967
- Headquarters: Jakarta, Indonesia
- Founding Document: ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration)
- Founding Members: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand
- Motto: One Vision, One Identity, One Community
- ASEAN Day: 8 August
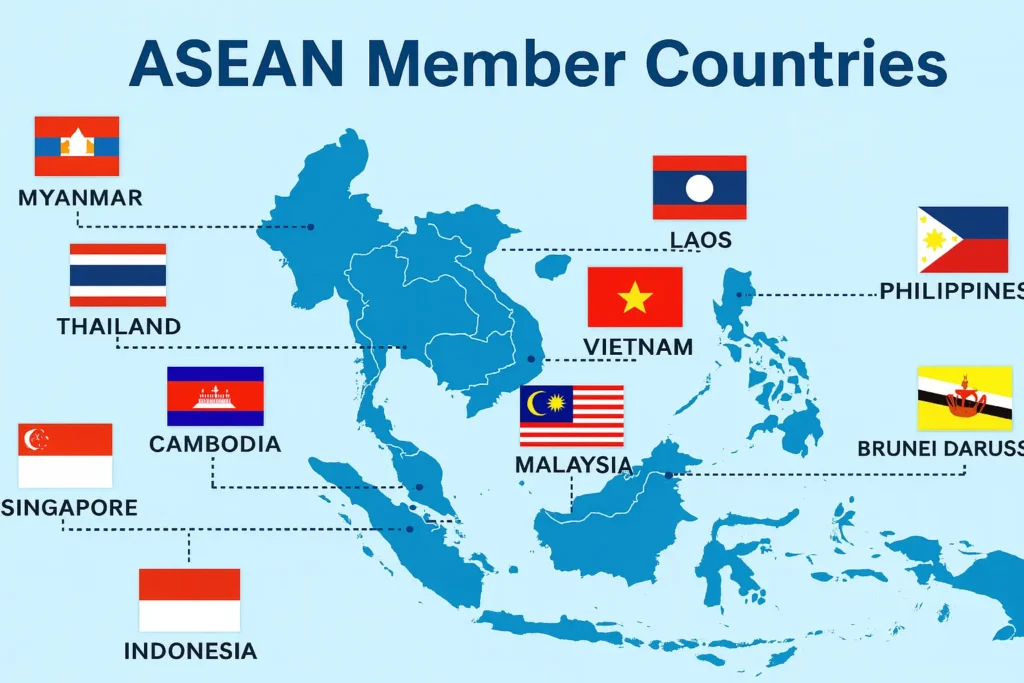
ASEAN Member States and Joining Dates
| Country | Commencement Date |
|---|---|
| Indonesia | 8 Aug 1967 |
| Malaysia | 8 Aug 1967 |
| Philippines | 8 Aug 1967 |
| Singapore | 8 Aug 1967 |
| Thailand | 8 Aug 1967 |
| Brunei Darussalam | 7 Jan 1984 |
| Viet Nam | 28 Jul 1995 |
| Lao PDR | 23 Jul 1997 |
| Myanmar | 23 Jul 1997 |
| Cambodia | 30 Apr 1999 |
ASEAN Charter
- Entered into force: 15 December 2008
- Purpose: To give ASEAN a legal status and institutional framework
- Key Provisions:
- New political commitment at top level
- Legal personality for ASEAN
- Enhanced role for Secretary-General
- Establishment of new ASEAN bodies
- Strengthened coordination among councils
Objectives of ASEAN
- To accelerate economic growth, social progress, and cultural development.
- To promote regional peace and stability through respect for justice and law.
- To strengthen cooperation in trade, education, and technology.
- To collaborate with international organizations.
- To maintain peace and neutrality in the region.
ASEAN Summit – The Highest Policy-Making Body
- The ASEAN Summit is the supreme decision-making body of ASEAN.
- It comprises Heads of State or Government of all ASEAN Member States.
- Frequency: Held twice a year, hosted by the Chair country.
- First ASEAN Summit:
- Date: 23–24 February 1976
- Venue: Bali, Indonesia
Functions of the ASEAN Summit
- Sets overall policy directions for ASEAN.
- Reviews the implementation of ASEAN objectives.
- Considers reports from the ASEAN Coordinating Council and Community Councils.
- Approves major agreements and initiatives.
ASEAN Coordinating Council (ACC)
- Established: 2008
- Members: Foreign Ministers of ASEAN States
- Functions:
- Prepare ASEAN Summit meetings
- Coordinate decisions of the Summit
- Approve Deputy Secretaries-General appointments
- Oversee the work of the ASEAN Secretariat
ASEAN Community Councils
ASEAN functions under three pillars, each managed by a Council:
- ASEAN Political-Security Community (APSC) – focuses on peace and stability.
- ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) – promotes free trade and integration.
- ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC) – works on education, environment, and culture.
ASEAN Symbols
Flag
- Colors: Blue (peace), Red (courage), White (purity), Yellow (prosperity)
- Symbol: Stalks of padi → dream of unity among Southeast Asian nations
- Circle: Represents ASEAN unity
Emblem
- Same colors and symbolism as the flag
- Represents a stable, peaceful, and dynamic ASEAN
Anthem: “The ASEAN Way”
- Represents unity and belonging among ASEAN people
Key Facts and Treaties
- Treaty of Amity and Cooperation (TAC): Signed in 1976 at the first summit, promoting non-interference and peaceful settlement of disputes.
- Southeast Asian Nuclear Weapon-Free Zone Treaty:
- Signed on 15 December 1995
- Became effective in 2001 after ratification by all members
- Aimed to make the region nuclear-weapon-free
Economic and Global Role
- Population: Over 600 million
- Land Area: 4.5 million sq km
- GDP (PPP, 2022): ~US$10.2 trillion (≈6.5% of global GDP)
- Includes some of the fastest-growing economies in the world.
- Plays a central role in regional trade blocs like RCEP and APEC.
Current ASEAN Chairmanship (2025)
- Chairmanship: Malaysia (Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim)
- Secretary-General: Kao Kim Hourn
Quick Revision Notes (for Exams)
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| ASEAN Founded | 8 August 1967, Bangkok |
| Founding Members | Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand |
| Current Members | 10 countries |
| First Summit | 1976, Bali |
| ASEAN Charter | 15 Dec 2008 |
| Motto | One Vision, One Identity, One Community |
| Anthem | The ASEAN Way |
| Headquarters | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| Chair 2025 | Malaysia |
| Secretary-General | Kao Kim Hourn |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When and where was ASEAN established?
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration).
Who are the founding members of ASEAN?
The five founding members of ASEAN are:
Indonesia
Malaysia
Philippines
Singapore
Thailand
When was the first ASEAN Summit held?
The first ASEAN Summit was held on 23–24 February 1976 in Bali, Indonesia.
What is the motto of ASEAN?
The ASEAN motto is: “One Vision, One Identity, One Community.”
What are the three pillars of the ASEAN Community?
The three pillars of the ASEAN Community are:
ASEAN Political–Security Community (APSC)
ASEAN Economic Community (AEC)
ASEAN Socio–Cultural Community (ASCC)
When did the ASEAN Charter come into force?
The ASEAN Charter came into force on 15 December 2008.
It provides a legal status and institutional framework for ASEAN’s functioning.
What is “The ASEAN Way”?
“The ASEAN Way” is the official anthem of ASEAN. It symbolizes unity, peace, and cooperation among member states and fosters a sense of regional identity and belonging.
Which country holds the ASEAN Chairmanship in 2025?
In 2025, the ASEAN Chairmanship is held by Malaysia, led by Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim.
The ASEAN Summit is the backbone of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations — driving unity, peace, and cooperation among its ten members. Its consistent efforts in political, economic, and socio-cultural integration have made ASEAN a key force in regional and global diplomacy.
Source: ASEAN Summit official website

