Biosphere Reserves in India 2025
Table of Contents
India’s network of Biosphere Reserves showcases a perfect blend of biodiversity conservation, community welfare, and sustainable development. Celebrated globally under the UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme, these reserves act as “living laboratories” where people and nature coexist harmoniously.
As of 2025, India has 18 Biosphere Reserves, covering 91,425 sq. km, out of which 13 are recognized by UNESCO. The recent inclusion of the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve (Himachal Pradesh) in 2025 further strengthens India’s position as a global conservation leader.
Key Facts on Biosphere Reserves in India
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Biosphere Reserves in India | 18 |
| Recognized by UNESCO | 13 |
| Total Area Covered | 91,425 sq. km |
| Funding Pattern | 60:40 (Central:State) and 90:10 for NE & Himalayan States |
| Administered by | MoEFCC under Conservation of Natural Resources & Ecosystems (CNRE) |
| Global Rank (Forest Area) | 9th (FAO 2025) |
| Annual Forest Gain Rank | 3rd (FAO 2025) |
What is a Biosphere Reserve?
A Biosphere Reserve is a designated area that protects terrestrial, marine, and coastal ecosystems while promoting sustainable human activities. It serves as a testing ground for research, education, and policy innovation on how humans can live in harmony with nature.
They are nominated by national governments and remain under the sovereign control of the state, integrating conservation with livelihood development.
Fact: Over 26 crore people live within biosphere reserves worldwide, which collectively protect an area equal to the size of Australia!
Structure of Biosphere Reserves
Each Biosphere Reserve has three functional zones:
| Zone | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Core Zone | Strictly protected area for biodiversity conservation. |
| Buffer Zone | Limited human activity allowed; supports research and education. |
| Transition Zone | Sustainable resource use, community involvement, and eco-development. |
List of 18 Biosphere Reserves in India (2025)
| No. | Biosphere Reserve | Location | Year | UNESCO Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nilgiri | Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka | 1986 | Yes |
| 2 | Nanda Devi | Uttarakhand | 1988 | Yes |
| 3 | Nokrek | Meghalaya | 1988 | Yes |
| 4 | Great Nicobar | Andaman & Nicobar Islands | 1989 | Yes |
| 5 | Gulf of Mannar | Tamil Nadu | 1989 | Yes |
| 6 | Manas | Assam | 1989 | No |
| 7 | Sundarbans | West Bengal | 1989 | Yes |
| 8 | Similipal | Odisha | 1994 | Yes |
| 9 | Dibru-Saikhowa | Assam | 1997 | No |
| 10 | Dehang-Debang | Arunachal Pradesh | 1998 | No |
| 11 | Pachmarhi | Madhya Pradesh | 1999 | Yes |
| 12 | Khangchendzonga | Sikkim | 2000 | Yes |
| 13 | Agasthyamalai | Kerala, Tamil Nadu | 2001 | Yes |
| 14 | Achanakmar-Amarkantak | MP, Chhattisgarh | 2005 | Yes |
| 15 | Great Rann of Kutch | Gujarat | 2008 | No |
| 16 | Cold Desert | Himachal Pradesh | 2009 | Yes (Added in 2025) |
| 17 | Seshachalam Hills | Andhra Pradesh | 2010 | No |
| 18 | Panna | Madhya Pradesh | 2011 | Yes |
Note for Aspirants: The Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve was recognized by UNESCO in 2025, bringing India’s total UNESCO-recognized reserves to 13.
Biosphere Reserves in India Map
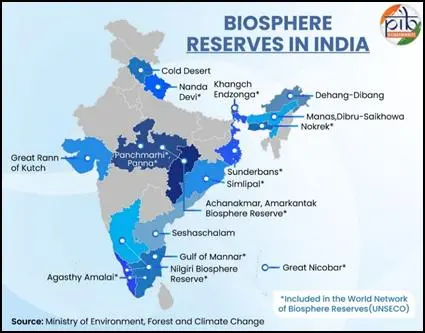
📸 Image Courtesy: Press Information Bureau (PIB), Government of India
Funding and Implementation
The Biosphere Reserve Scheme operates under a Centrally Sponsored Model:
- 60:40 cost-sharing between Centre and State.
- 90:10 funding for Himalayan and NE States.
Budget allocation for biodiversity conservation has doubled — from ₹5 crore (2024–25) to ₹10 crore (2025–26).
This ensures stronger focus on eco-development, community-based resource management, and alternative livelihoods to reduce pressure on core ecosystems.
India’s Commitment to Global Conservation
India’s Biosphere Reserve Programme is aligned with UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) goals:
- Conserve biological and cultural diversity.
- Promote research and innovation in sustainable practices.
- Integrate scientific and traditional knowledge.
- Support livelihoods for local and tribal communities.
With 18 reserves across diverse ecosystems—mountains, coasts, forests, and deserts—India reflects the vision of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”—the world as one family.
Complementary National Initiatives
Biosphere Reserves are supported by multiple conservation programmes:
- Project Tiger (1973) – 50 years of tiger conservation success.
- Project Elephant (1992) – Safeguarding India’s elephant corridors.
- Green India Mission (2014) – Enhancing forest cover and carbon sinks.
- Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats (IDWH) – Supports state-led conservation.
- National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP) – Framework for sustainable use of biological resources.
These initiatives together strengthen India’s ecosystem resilience and promote inclusive growth.
India’s Forest Achievements (FAO 2025)
| Parameter | India’s Global Rank |
|---|---|
| Total Forest Area | 9th |
| Annual Forest Gain | 3rd |
| Forest Area Coverage | 24.62% of geographical area |
| Forest Jobs Created | Over 2 crore livelihoods |
FAQs on Biosphere Reserves in India
How many Biosphere Reserves are there in India in 2025?
India has 18 Biosphere Reserves, out of which 13 are recognized by UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR).
Which is the latest Biosphere Reserve added to UNESCO’s list?
The Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve in Himachal Pradesh was included in 2025.
What is the difference between a National Park and a Biosphere Reserve?
National Parks focus solely on wildlife protection, while Biosphere Reserves integrate biodiversity conservation with sustainable human development.
Which is India’s largest Biosphere Reserve?
The Gulf of Kutch (Gujarat) is the largest, covering over 12,454 sq. km.
What is the funding ratio for Biosphere Reserves in India?
60:40 for most states and 90:10 for North Eastern and Himalayan states.
How many biosphere reserves in India are recognized by UNESCO?
Out of 18, a total of 13 are part of the UNESCO World Network.
What is the role of the Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme?
The UNESCO MAB Programme fosters international cooperation for biodiversity conservation, education, and research on sustainable living.
For Aspirants
For aspirants of APPSC, UPSC, and SSC, this topic is a must-read under Environment, Geography, and Current Affairs. Key questions like “How many Biosphere Reserves in India?” and “Which are UNESCO-recognized reserves?” are frequently asked in Prelims and Mains.
Remember: Biosphere Reserves embody India’s vision of “Sustainable Living in Harmony with Nature.”
Source: PIB