7 Nanometer Processor
Table of Contents
Why the 7 Nanometer Processor Matters
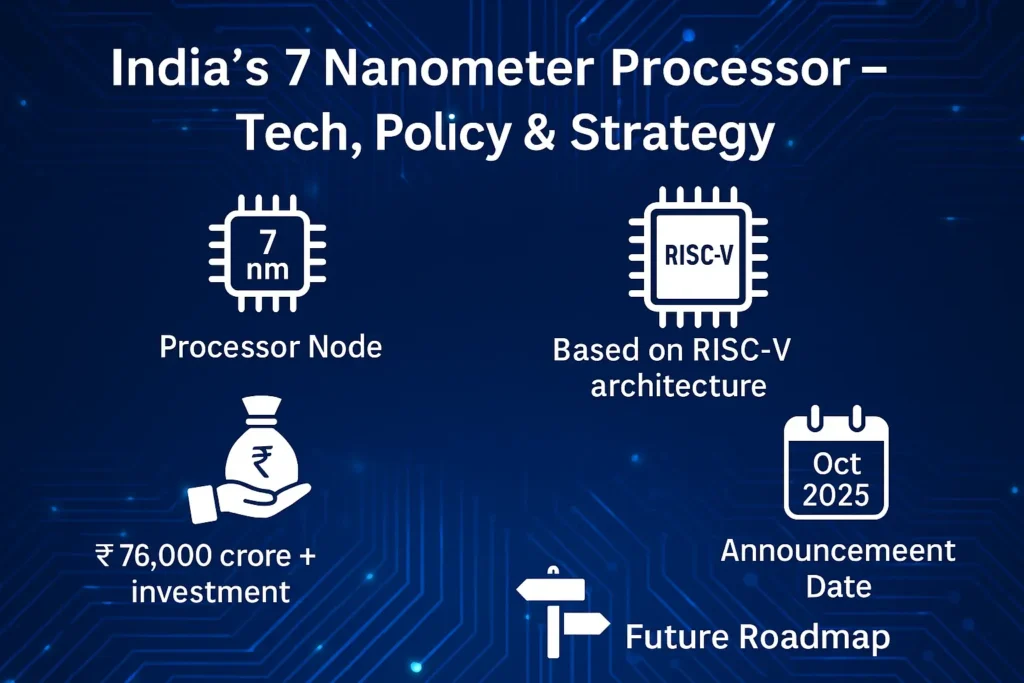
Semiconductor design is foundational to modern technology. The term “7 nanometer processor” refers to a chip built using 7 nm process technology, allowing greater transistor density, lower power consumption, and higher performance. When Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT Madras) announced an indigenous project to develop a 7 nm processor on 18 October 2025, it marked India’s entry into advanced-node chip design — a big step in its ambition to become a major player in the global semiconductor ecosystem.
Key Facts: The Initiative
- The project is part of India’s broader journey in indigenous chip design, especially via the SHAKTI initiative (open-source RISC-V architecture) started in 2013.
- It is led by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) under the national semiconductor policy framework and the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM).
- The target application areas include servers, communications, defence, AI and 5G infrastructure — sectors that need high-end processors.
- India has approved large investments under ISM (over ₹1.6 lakh crore across states) and supports academic-industry linkages (288 institutions under the Design Linked Incentive scheme).
Why India Moving to 7 nm is Strategic
1. Performance & Efficiency
A 7 nm chip allows many more transistors per unit area compared to older nodes (e.g., 14 nm or 10 nm), enabling high performance with lower power — crucial for data centres, AI, 5G.
2. Indigenous Capability
By mastering 7 nm design, India strengthens its self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat) and reduces dependence on imports of critical chips.
3. Supply-Chain Integration
This design capability complements the India Semiconductor Mission’s aim to build end-to-end chip manufacturing(design → fab → packaging) in India.
4. Global Value Chain
With advanced node R&D, India positions itself among nations like Taiwan, South Korea, and the US in chip innovation, making it a trusted global partner.
What Students Should Focus On (Exam Point-Of-View)
- Definition: Understand “7 nanometer processor” as a chip fabricated using a process technology where transistor features measure ~7 nm.
- Architecture: Know that India uses RISC-V (open-source instruction set) via the SHAKTI initiative.
- Policy Linkage: The project aligns with MeitY, ISM, and the national mission to build a semiconductor ecosystem.
- Applications: Servers, 5G/6G, AI, defence systems.
- Economic Impact: Large investments, job creation in high-skill sectors, strengthening of India’s tech ecosystem.
- Recent Date: The announcement of the 7 nm initiative on 18 October 2025 by Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw.
- Future Roadmap: Sub-7 nm nodes, chip packaging, design tools, fab creation in India.
7 Nanometer Processor Roadmap
- India sanctioned 24 chip-design projects and 87 companies now use advanced design tools.
- The India Semiconductor Mission has a budget of ~₹76,000 crore and supports multi-state projects.
- Next steps include building test-and-packaging facilities, moving to sub-7 nm nodes, and attracting global investments.
- Students may see questions such as: Which node size has India announced as its next milestone? or Which architecture underlies India’s SHAKTI processor family?
The development of a 7 nanometer processor in India is not just a technical milestone — it’s a strategic statement. For students and exam aspirants, this topic bridges science & technology, industrial policy, and India’s development story. Knowing its components, policy linkages, and implications gives you an edge in current-affairs and technology-governance sections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a 7 nanometer processor?
A 7 nanometer processor is a microchip built using semiconductor manufacturing technology where each transistor measures about 7 nanometers (nm). The smaller node allows more transistors to fit on a chip, improving speed, efficiency, and performance while using less power.
Which institute developed India’s 7 nanometer processor?
The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras developed the indigenous 7 nanometer processor under the SHAKTI initiative, supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
When was India’s 7 nanometer processor announced?
It was officially announced on 18 October 2025 by Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw, marking India’s entry into advanced-node semiconductor design.
What is special about the 7 nanometer processor developed in India?
India’s 7 nm processor is based on open-source RISC-V architecture under the SHAKTI project. It is designed for servers, AI, 5G, and defence systems, representing a leap toward Atmanirbhar Bharat in high-end chip technology.
What is the SHAKTI project?
SHAKTI is India’s open-source processor development initiative, started in 2013 at IIT Madras. It uses RISC-V architecture to design processors that can be freely adopted by startups, researchers, and industries for innovation and custom applications.
How does a 7 nm processor differ from a 14 nm processor?
A 7 nm processor has smaller transistors, enabling up to double the performance and lower power consumption than a 14 nm chip. This efficiency makes it ideal for high-performance computing, AI, and mobile devices.
What is RISC-V and why is it important for India?
RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) that allows countries to design processors without paying licensing fees to global chip giants. For India, it ensures strategic autonomy and promotes domestic semiconductor innovation.
How does the 7 nanometer processor support India’s Semiconductor Mission?
The project aligns with the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), which has an outlay of ₹76,000 crore to create an end-to-end semiconductor ecosystem — from chip design and testing to packaging and fabrication.
Source: PIB